






Selected Articles from the
November 2001 Odyssey
Editor: Terry Hancock
- Mars Odyssey Infrared Images, NASA
- First Observation of Black Hole Energy Extraction, NASA
- The Surf Report, Diane Rhodes
Mars Odyssey Infrared Images
A NASA Press Release
NASA's 2001 Mars Odyssey gave mission managers a real treat this Halloween with its first look at the Red Planet. It's a thermal infrared image of the Martian southern hemisphere that captures the polar carbon dioxide ice cap at a temperature of about -120°C.The spacecraft first entered orbit around Mars last week after a six-month, 285 million-mile journey.
The image, taken as part of the calibration process for the instrument, shows the nighttime temperatures of Mars, demonstrating the "night-vision" capability of the camera system to observe Mars, even when the surface is in darkness.
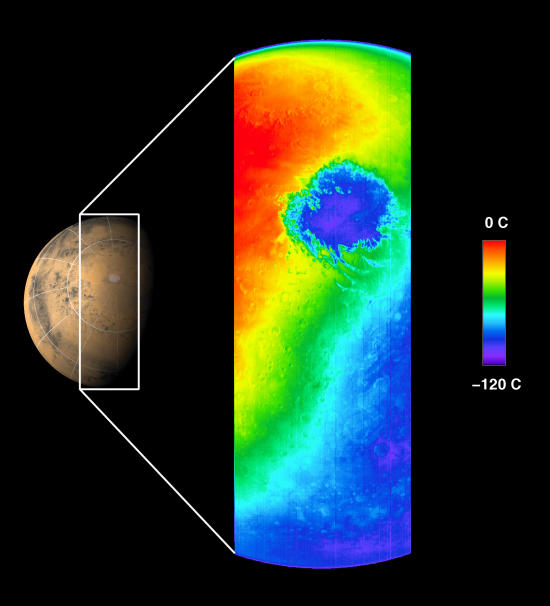 |
| False color imate of Mars in infrared. NASA/JPL/Caltech. Click to enlarge. |
``This spectacular first image of Mars from the 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft is just a hint of what's to come,'' said Dr. Ed Weiler, Associate Administrator for Space Science at NASA Headquarters in Washington. ``After we get Odyssey into its final orbit it will be much closer to Mars than when it took this image, and we'll be able to tell whether or not there are any hot springs on Mars, places where liquid water may be close to the surface. If there are any such locations they would be places we might like to explore on future missions.''
The image covers a length of more than 6,500 km, spanning the planet from limb to limb, with a resolution of approximately 5.5 kilometers per pixel, at the point directly beneath the spacecraft.
The spacecraft was about 22,000 km above the planet looking down toward the south pole of Mars when the image was taken.
It is late spring in the Martian southern hemisphere. The extremely cold, circular feature shown in blue is the Martian south polar carbon dioxide ice cap , which is more than 900 km in diameter at this time and will continue to shrink as summer progresses. Clouds of cooler air blowing off the cap can be seen in orange extending across the image.
JPL manages the 2001 Mars Odyssey mission for NASA's Office of Space Science. The thermal-emission imaging system was developed at Arizona State University, Tempe, with Raytheon Santa Barbara Remote Sensing, Santa Barbara, Calif. Lockheed Martin Astronautics, Denver, is the prime contractor for the project, and developed and built the orbiter. Mission operations are conducted jointly from Lockheed Martin and from JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.
File translated from TEX by TTH, version
2.25.
On 27 Jan 2002, 17:42.
Copyright © 1998-2003 Organization for the Advancement of Space Industrialization and Settlement. All Rights Reserved.